
ANXIETY INSOMNIA ICD 10 MANUAL
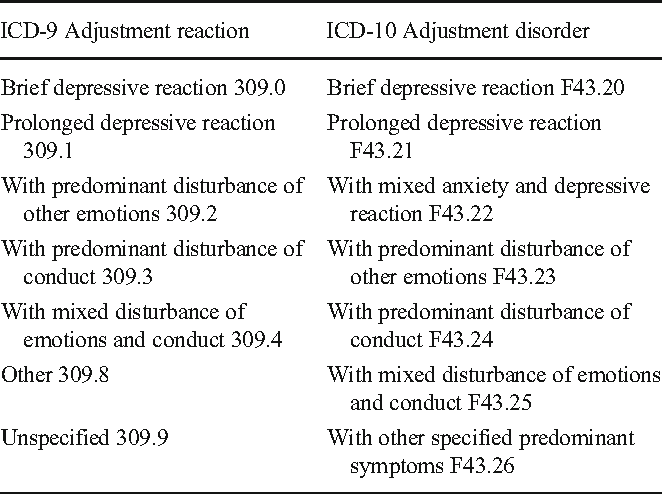
This is partly attributable to the fact that sleep disturbance is a cardinal diagnostic criterion for GAD in both the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (Slade & Andrews, 2001).
ANXIETY INSOMNIA ICD 10 FULL
Insomnia that presents as a symptomatic complaint, yet does not meet full diagnostic criteria, has been estimated to occur in approximately 25–30% of adults in the general population and has been associated with significant levels of occupational impairment (Kessler et al. Insomnia occurs even more frequently in the general population, with prevalence rates in the range of 5–15%, even when the diagnosis is restricted to severe complaints of disturbance in sleep onset or sleep maintenance that persist for >2 wk and are associated with significant impairment in functioning (Ohayon, 2002). Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a common disorder with a lifetime prevalence in the community estimated to range from 2.8 to 5.7% (Alonso & Lepine, 2007 Kessler et al. Insomnia is a common component of the clinical presentation of GAD and pregabalin appears to be an efficacious treatment for this often chronic and disabling symptom.Īnxiety, insomnia, pregabalin, sleep disturbance Introduction

However, dose-related sedation is reported, typically in the first 2 wk of treatment, in approximately 10–30% of patients, depending on the dose used and the speed of titration. In patients with GAD, improvement in sleep has been found to be associated with a reduction in daytime sleepiness. Results of a mediational analysis suggest that 53% of the effect of pregabalin on sleep disturbance was due to a direct effect and 47% was due to an indirect effect, mediated through prior reduction in anxiety symptom severity. Treatment with pregabalin is associated with improvement in all forms of insomnia and improvement in sleep has been found to be correlated with reduction in functional impairment and improvement in quality of life on subjective global measures. Treatment with pregabalin has been found to be associated with significant improvement in GAD-related sleep disturbance across seven placebo-controlled clinical trials. Pregabalin binds to a membrane α2δ subunit protein to inhibit release in excited central nervous system neurons of neurotransmitters implicated in pathological anxiety. The hypothesized mechanism of action of pregabalin is distinctly different from other anxiolytics. This review summarizes the results of clinical trials and pooled analyses that provide data on pregabalin's effect on sleep disturbance in patients diagnosed with GAD. Sleep disturbance is a cardinal symptom in both DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
